OPICS Quickstart
Contents
OPICS Quickstart¶
Installing OPICS¶
Installing from source¶
Download the OPICS source code.
git clone https://github.com/jaspreetj/opics
Install the OPICS package using pip.
pip install -e ./opics
Once the package is installed, it can be imported using:
import opics as op
____ ____ _______________
/ __ \/ __ \/ _/ ____/ ___/
/ / / / /_/ // // / \__ \
/ /_/ / ____// // /___ ___/ /
\____/_/ /___/\____//____/
OPICS version 0.3.1
OPICS Libraries¶
Listing available libraries¶
The package does not come with any component libraries pre-installed. You can select and download available libraries from the library catalogue.
library_catalogue = op.libraries.library_catalogue
print(f"Available Libraries: {[_ for _ in library_catalogue.keys()]} ")
Available Libraries: ['ebeam', 'shuksan']
Downloading libraries¶
The OPICS libraries are downloaded by passing in library_name, library_url, and library_path to the libraries.download_library module. The module returns True if the library is downloaded successfully.
library = library_catalogue["ebeam"]
import os
installation_path = os.path.join(os.path.join(os.environ['USERPROFILE']), 'Desktop\\delete')
op.libraries.download_library(
library_name=library["name"],
library_url=library["dl_link"],
library_path=installation_path,
)
# reload libraries
import importlib
importlib.reload(op.libraries)
Download start
Download finished.
<module 'opics.libraries' from 'c:\\users\\jeida\\documents\\github\\dev-jaspreetj\\opics\\opics\\libraries\\__init__.py'>
List installed libraries¶
op.libraries.installed_libraries
['ebeam']
List library components¶
op.libraries.ebeam.components_list
['BDC',
'DC_halfring',
'GC',
'Switch',
'TunableWG',
'Waveguide',
'Y',
'ebeam_y_1550',
'ebeam_gc_te1550',
'ebeam_wg_integral_1550']
Remove libraries¶
Any of the installed libraries can be removed using the libraries.remove_library module.
op.libraries.remove_library("ebeam")
importlib.reload(op.libraries)
print(op.libraries.installed_libraries)
[]
#reinstall ebeam library
op.libraries.download_library(
library_name=library["name"],
library_url=library["dl_link"],
library_path=installation_path,
)
importlib.reload(op.libraries)
print(op.libraries.installed_libraries)
Download start
Download finished.
['ebeam']
Library components¶
Let’s take a look at the library components.
ebeam_lib = op.libraries.ebeam
Listing library components
ebeam_lib.components_list
['BDC',
'DC_halfring',
'GC',
'Switch',
'TunableWG',
'Waveguide',
'Y',
'ebeam_y_1550',
'ebeam_gc_te1550',
'ebeam_wg_integral_1550']
Let’s take a look inside a component for more information on its parameters and layout, such as port locations.
ebeam_lib.BDC?
Setting up a simulation¶
The network module is used to define a circuit, add and connect components. The network module takes network_id and f as inputs. If no f or frequency data points specified, the network module uses the default value specified in opics.globals.F.
from opics import Network
from opics.globals import C
import numpy as np
freq = np.linspace(C * 1e6 / 1.5, C * 1e6 / 1.6, 2000)
circuit = Network(network_id="circuit_name", f=freq)
Once an empty network is defined. We can start by adding components.
input_gc = circuit.add_component(ebeam_lib.GC)
y = circuit.add_component(ebeam_lib.Y)
wg2 = circuit.add_component(ebeam_lib.Waveguide, params=dict(length=0e-6))
wg1 = circuit.add_component(ebeam_lib.Waveguide, params={"length":15e-6})
y2 = circuit.add_component(ebeam_lib.Y)
output_gc = circuit.add_component(ebeam_lib.GC)
We can also define custom port names for components for easy reference.
input_gc.set_port_reference(0, "input_port")
output_gc.set_port_reference(0, "output_port")
Connect components using the Network.connect module.
circuit.connect(input_gc, 1, y, 0)
circuit.connect(y, 1, wg1, 0)
circuit.connect(y, 2, wg2, 0)
circuit.connect(y2, 0, output_gc, 1)
circuit.connect(wg1, 1, y2, 1)
circuit.connect(wg2, 1, y2, 2)
Simulate the network/circuit
circuit.simulate_network()
<opics.components.componentModel at 0x16a72705580>
Plot the simulated response
circuit.sim_result.plot_sparameters(show_freq=False)
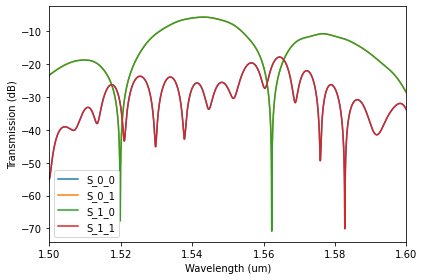
An interactive plot can be spawned by enabling the interactive option.
circuit.sim_result.plot_sparameters(show_freq=False, interactive=True)
